There are many career opportunities in the maritime logistics industry. This industry is highly specialized and requires a lot training. Websites such as Shiptalk, Hellenic Shipping News and others can provide more information. It's a rewarding job.
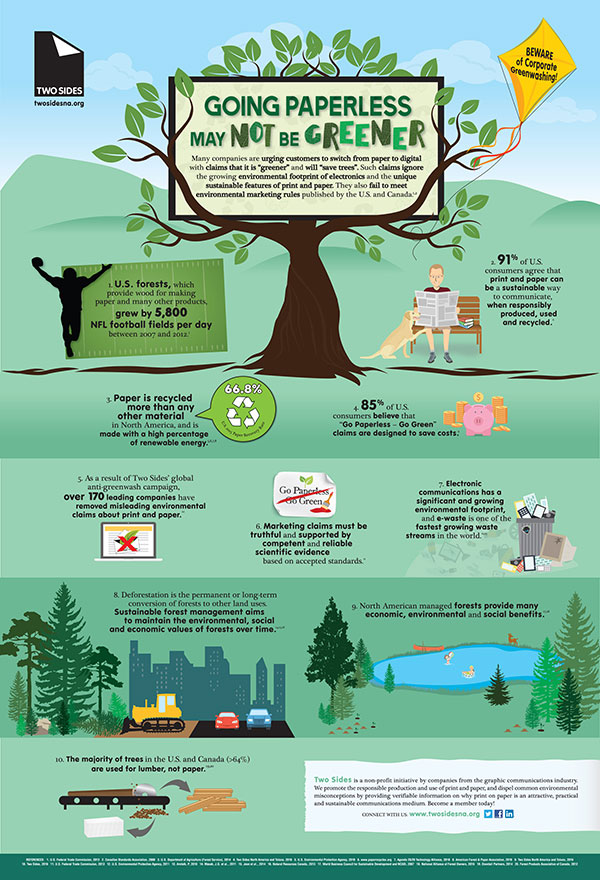
Bulk cargo is the largest part of the maritime industry. It includes general cargo ships and ore and coal carriers, as well tankers and container vessels. In the past, the loading and unloading process took much longer than it does today. Because of this, average ships spent more time at dock than at sea. This is due in large part to technological improvements that have simplified the process. Shipping costs can be kept low due to the efficiency of scale.
In the 1950s, when containerisation revolutionized freight routes, a number of new services were created. This has been possible thanks to a number of technologies, such as computer-aided Navigation, global positioning system, and automation. For instance, self-unloading ships have become a reality. Despite some recent declines in the shipping sector, it is still a highly lucrative industry to be part of.
As with other industries, maritime logistics jobs are available in a variety of positions. For example, there is a need for logistics/embarkation specialists who are tasked with preparing supplies for embarkation. They may also be involved in force deployment planning and execution. This is a complicated role that requires knowledge of all relevant technology.
Representatives from shipping lines are responsible for providing competitive pricing and maintaining an efficient pricing database. To obtain the best possible rates, the person will need to contact airlines as well as co-loaders. He or she might also be asked to organize company information for tender procedures. This position requires knowledge of different ports.
A maritime logistics job requires an in-depth knowledge of many subjects, just like any other industry. This is due to the global nature of the industry. The fact that the majority of vessels are owned and operated by companies from outside the United States can complicate matters. Thus, opportunities for sponsorship are limited. You can research the industry on websites like Shiptalk and find marine logistics jobs. If you are interested, you might want to look into an apprenticeship program. These are also open to military personnel. You will be awarded a certificate upon completion of the program and an industry-specific knowledge.

The next step in a career offering a lot of perks and a high salary is a job as a maritime logistics professional. Centerline Logistics, a major provider of marine transportation in the United States, seeks QMED/Oilers who have two years experience in marine diesels.
FAQ
What does warehouse refer to?
A warehouse or storage facility is where goods are stored before they are sold. It can be an indoor space or an outdoor area. It could be one or both.
What does it take for a logistics enterprise to succeed?
You need to have a lot of knowledge and skills to manage a successful logistic business. Effective communication skills are necessary to work with suppliers and clients. You will need to know how to interpret data and draw conclusions. You must be able to work well under pressure and handle stressful situations. You need to be innovative and creative to come up with new ways to increase efficiency. You must be a strong leader to motivate others and direct them to achieve organizational goals.
To meet tight deadlines, you must also be efficient and organized.
Why is logistics important in manufacturing?
Logistics are an essential component of any business. They can help you achieve great success by helping you manage product flow from raw material to finished goods.
Logistics also play a major role in reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
What is the distinction between Production Planning or Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP) is the process of determining what needs to be produced at any given point in time. This is done through forecasting demand and identifying production capacities.
Scheduling refers to the process of allocating specific dates to tasks in order that they can be completed within a specified timeframe.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics?
The acronym 7R's of Logistic is an acronym that stands for seven fundamental principles of logistics management. It was developed and published by the International Association of Business Logisticians in 2004 as part of the "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The following letters form the acronym:
-
Responsible - to ensure that all actions are within the legal requirements and are not detrimental to others.
-
Reliable - Have confidence in your ability to fulfill all of your commitments.
-
Reasonable - use resources efficiently and don't waste them.
-
Realistic - consider all aspects of operations, including cost-effectiveness and environmental impact.
-
Respectful - Treat people fairly and equitably
-
Be resourceful: Look for opportunities to save money or increase productivity.
-
Recognizable - Provide value-added services to customers
Statistics
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing is a management style that aims to increase efficiency and reduce waste through continuous improvement. It was created in Japan by Taiichi Ohno during the 1970s and 80s. He received the Toyota Production System award (TPS), from Kanji Toyoda, founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the first book on lean manufacturing in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes the elimination and minimization of waste in the value stream. Lean manufacturing is also known as just in time (JIT), zero defect total productive maintenance(TPM), and five-star (S). Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing is a way for companies to achieve their goals faster, improve product quality, and lower costs. Lean manufacturing can be used to manage all aspects of the value chain. Customers, suppliers, distributors, retailers and employees are all included. Lean manufacturing can be found in many industries. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Lean manufacturing is based on five principles:
-
Define value - Find out what your business contributes to society, and what makes it different from other competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Remove any activity which doesn't add value to your supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize and simplify - Make your processes as consistent as possible.
-
Build Relationships- Develop personal relationships with both internal as well as external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing isn't a new concept in business, it has gained popularity due to renewed interest in the economy after the 2008 global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. Economists think that lean manufacturing is a crucial factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include higher customer satisfaction, lower inventory levels, lower operating expenses, greater productivity, and improved overall safety.
The principles of lean manufacturing can be applied in almost any area of an organization. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three types of lean manufacturing.
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing, (JIT): This kind of lean manufacturing is also commonly known as "pull-systems." JIT means that components are assembled at the time of use and not manufactured in advance. This strategy aims to decrease lead times, increase availability of parts and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing: ZDM ensures that no defective units leave the manufacturing plant. Repairing a part that is damaged during assembly should be done, not scrapping. This applies to finished products, which may need minor repairs before they are shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement: Continuous Improvement aims to improve efficiency by continually identifying problems and making adjustments to eliminate or minimize waste. It involves continuous improvement of processes, people, and tools.