
The five s's are the key to lean manufacturing. They are Standardize. Straighten. Shine. and Sustain. Here are some steps you should follow. To maximize your lean transformation, you must train your frontline operators and team leaders.
Standardize
Clean up and organize your workspace as the first step in the 5S Process. While this may seem like an insignificant task at first, standardizing the process can make it easier. To help you create a consistent approach with 5S tasks, use checklists, visual cues and checklist template.
These five s’s of lean can help improve the productivity and efficiency of your workplace. This will encourage staff to be organised and make their work easier. This will help improve your efficiency by organizing your work area. These five s’s are helpful for improving safety in the workplace. A well-organized space will prevent accidents, minimize mistakes and increase the chance of producing productive work.
Straighten
Not having to do it all is necessary to achieve your 5 S's of Lean. Companies can improve their business processes and practice lean principles consistently. Workers will be more likely to find the right components by organizing them in an assembly line. This will reduce time spent searching for missing parts and increase safety and efficiency in the company's workflow.
You can also reduce the amount of items that are in each work area and save money on consumables. This can help you reduce your office supply bills. Straightening your work cells will not only save money but also improve the quality and safety of your production processes.
Shine
Shine is a step that inspects the workspace and points out potential problems. Shine inspects tools and equipment to help improve flow and reduce waste. Shine improves the maintenance of a workspace and enables workers to see if there is a problem before it hampers production. It also helps to standardize the layout of a work area to increase output.
Shine is a tool that can be used to lean manufacturing. This technique streamlines and automates work processes to reduce waste and increase efficiency. It can be applied to any industry, including manufacturing. In this way, it applies the 5S principles across a business. It helps companies reduce unnecessary inventory, work-in-progress, and supply stocks.
Keep it up
Re-instating a standardized system in a facility is key to maintaining the 5 S's of Lean. This is a continuous process that should be repeated until the facility functions at its best. This is why employees need to be trained in 5S auditing.
The 5S approach emphasizes reducing waste, optimizing productivity, and keeping a clean, orderly workplace. It is basically a way to organize workplaces according to the five principles of Toyota Production System. This system was created by Hiroyuki Hirano, a post-war Japanese engineer, to increase efficiency in manufacturing plants.
FAQ
What are the requirements to start a logistics business?
It takes a lot of skills and knowledge to run a successful logistics business. For clients and suppliers to be successful, you need to have excellent communication skills. It is important to be able to analyse data and draw conclusions. You must be able manage stress and pressure under pressure. You need to be innovative and creative to come up with new ways to increase efficiency. You need to have strong leadership qualities to motivate team members and direct them towards achieving organizational goals.
You must be organized to meet tight deadlines.
What is the difference between a production planner and a project manager?
The primary difference between a producer planner and a manager of a project is that the manager usually plans and organizes the whole project, while a production planner is only involved in the planning stage.
What is the difference in Production Planning and Scheduling, you ask?
Production Planning (PP), is the process of deciding what production needs to take place at any given time. Forecasting demand is one way to do this.
Scheduling involves the assignment of dates and times to tasks in order to complete them within the timeframe.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics?
The acronym 7Rs of Logistics refers to the seven core principles of logistics management. It was developed by the International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL) and published in 2004 as part of its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management" series.
The acronym is made up of the following letters:
-
Responsible - ensure that all actions taken are within legal requirements and are not harmful to others.
-
Reliable – have faith in your ability and capability to keep promises.
-
Reasonable - use resources efficiently and don't waste them.
-
Realistic - Take into consideration all aspects of operations including cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, and other factors.
-
Respectful: Treat others with fairness and equity
-
Be resourceful: Look for opportunities to save money or increase productivity.
-
Recognizable is a company that provides customers with value-added solutions.
What is production planning?
Production Planning refers to the development of a plan for every aspect of production. This document will ensure everything is in order and ready to go when you need it. This document should include information about how to achieve the best results on-set. This includes shooting schedules, locations, cast lists, crew details, and equipment requirements.
It is important to first outline the type of film you would like to make. You may already know where you want the film to be shot, or perhaps you have specific locations and sets you wish to use. Once you have determined your scenes and locations, it is time to start figuring out the elements that you will need for each scene. You might decide you need a car, but not sure what make or model. In this case, you could start looking up cars online to find out what models are available and then narrow your choices by choosing between different makes and models.
After you have chosen the right car, you will be able to begin thinking about accessories. You might need to have people in the front seats. You might also need someone to help you get around the back. Maybe you'd like to change the interior from black to a white color. These questions will help guide you in determining the ideal look and feel for your car. The type of shots that you are looking for is another thing to consider. Do you want to film close-ups, or wider angles? Maybe you want to show your engine or the steering wheel. These things will help you to identify the car that you are looking for.
Once you've determined the above, it is time to start creating a calendar. The schedule will show you when to begin shooting and when to stop. Each day will include the time when you need to arrive at the location, when you need to leave and when you need to return home. Everyone knows exactly what they should do and when. Hire extra staff by booking them ahead of time. You should not hire anyone who doesn't show up because of your inaction.
Also, consider how many days you will be filming your schedule. Some projects only take one or two days, while others may last weeks. When creating your schedule, be aware of whether you need more shots per day. Multiple takes of the same location will lead to higher costs and take more time. If you are unsure if you need multiple takes, it is better to err on the side of caution and shoot fewer takes rather than risk wasting money.
Another important aspect of production planning is setting budgets. A realistic budget will help you work within your means. Keep in mind that you can always reduce your budget if you face unexpected difficulties. But, don't underestimate how much money you'll spend. Underestimating the cost will result in less money after you have paid for other items.
Production planning is a detailed process. But, once you understand the workings of everything, it becomes easier for future projects to be planned.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use lean manufacturing in the Production of Goods
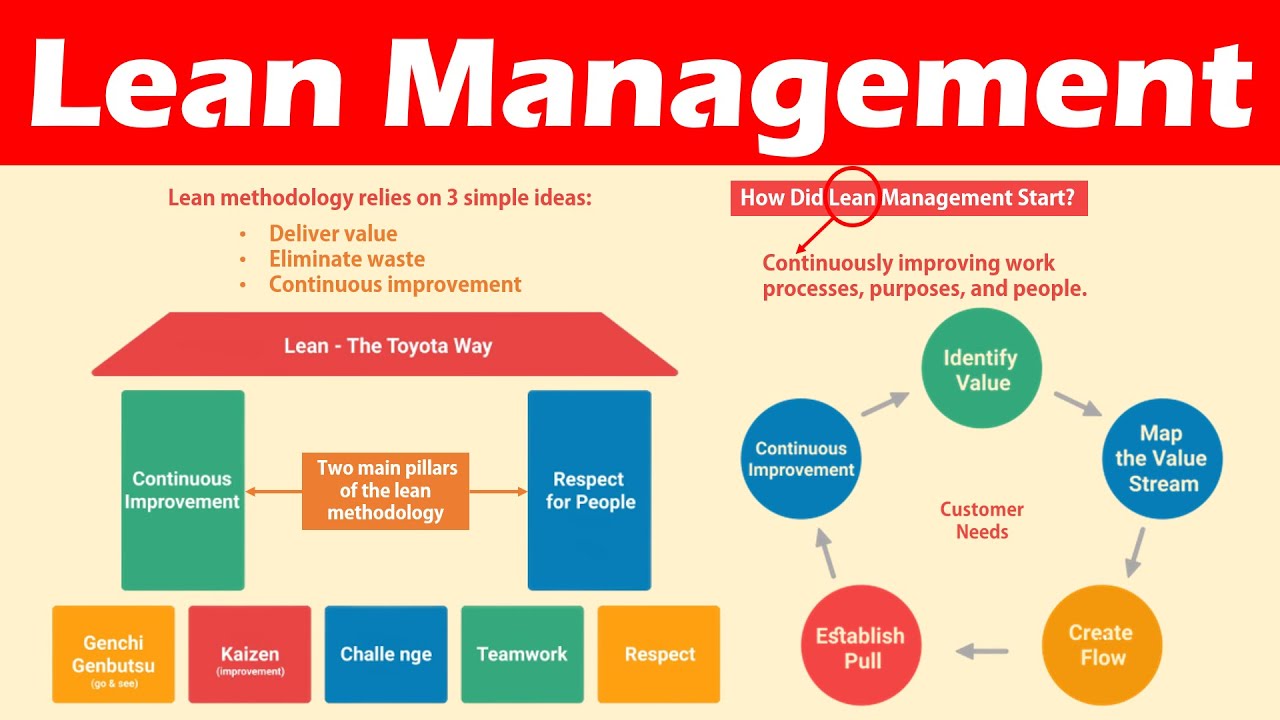
Lean manufacturing (or lean manufacturing) is a style of management that aims to increase efficiency, reduce waste and improve performance through continuous improvement. It was first developed in Japan in the 1970s/80s by Taiichi Ahno, who was awarded the Toyota Production System (TPS), award from KanjiToyoda, the founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the "The Machine That Changed the World", the first book about lean manufacturing. It was published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes the elimination of defects and waste throughout the value stream. Just-in-time (JIT), zero defect (TPM), and 5S are all examples of lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing emphasizes reducing non-value-added activities like inspection, rework and waiting.
In addition to improving product quality and reducing costs, lean manufacturing helps companies achieve their goals faster and reduces employee turnover. Lean Manufacturing is one of the most efficient ways to manage the entire value chains, including suppliers and customers as well distributors and retailers. Lean manufacturing is widely used in many industries. Toyota's philosophy, for example, is what has enabled it to be successful in electronics, automobiles, medical devices, healthcare and chemical engineering as well as paper and food.
Five principles are the basis of lean manufacturing:
-
Define Value - Identify the value your business adds to society and what makes you different from competitors.
-
Reduce waste - Stop any activity that isn't adding value to the supply chains.
-
Create Flow – Ensure that work flows smoothly throughout the process.
-
Standardize & simplify - Make processes consistent and repeatable.
-
Build relationships - Develop and maintain personal relationships with both your internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing isn’t new, but it has seen a renewed interest since 2008 due to the global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean manufacturing techniques to help them become more competitive. Some economists even believe that lean manufacturing can be a key factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced inventory levels as well as lower operating costs.
Lean manufacturing can be applied to almost every aspect of an organization. However, it is particularly useful when applied to the production side of an organization because it ensures that all steps in the value chain are efficient and effective.
There are three types of lean manufacturing.
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing, (JIT): This kind of lean manufacturing is also commonly known as "pull-systems." JIT is a method in which components are assembled right at the moment of use, rather than being manufactured ahead of time. This method reduces lead times, increases availability, and decreases inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM): ZDM focuses on ensuring that no defective units leave the manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This also applies to finished products that need minor repairs before being shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement: Continuous Improvement aims to improve efficiency by continually identifying problems and making adjustments to eliminate or minimize waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.