
An industrial manager is an engineer who integrates different engineering processes to create an efficient management system. An industrial manager helps to integrate these engineering processes into a single, integrated management system. Here are some facts about this job. Here are the requirements and benefits of becoming an industrial manager. If you are looking for a challenging but rewarding career, this could be the career for your. Continue reading to learn about the career.
Job description
An industrial manager is responsible for overseeing the production and manufacturing of goods and services. While this job may cover all aspects of the production process, it will also focus on how to source raw materials and implement equipment. Industrial production managers must be computer literate, as computers increasingly play a key role in the coordination of various departments, suppliers, and clients. Industrial production managers should be knowledgeable about the latest management techniques and production technologies. Managers are often involved in professional organizations and attend trade shows and industry conferences. They also take courses to become certified in their fields.
In addition to overseeing manufacturing processes, industrial managers coordinate the activities of various departments within a company. They ensure production lines run efficiently and meet customer needs in terms quality and time. They may also supervise staffing levels or change production levels as required to minimize inventory. They might also coordinate with other departments and oversee quality control programs. Majority of their responsibilities involve managing people. This involves identifying, training, motivating and motivating employees.
Education required
For industrial managers, a bachelor's level in business administration, management, engineering or other related fields is not enough. Some employers prefer candidates with a background or education in these areas. Also, industrial managers must be computer-literate. Computers have become an integral part in manufacturing. They can help coordinate production between departments as well as suppliers and clients. Interested individuals should obtain the proper education and experience to excel in this field.
Many industrial production managers begin their careers as workers, and then move up to supervisory positions. Most professionals need to have a college degree or equivalent in business management to be able to move up to the position of industrial manager. Some entry-level workers might be able to get this education while on the job or through classes sponsored by their employers. However, managers must have two to five year of relevant experience before becoming a manager.
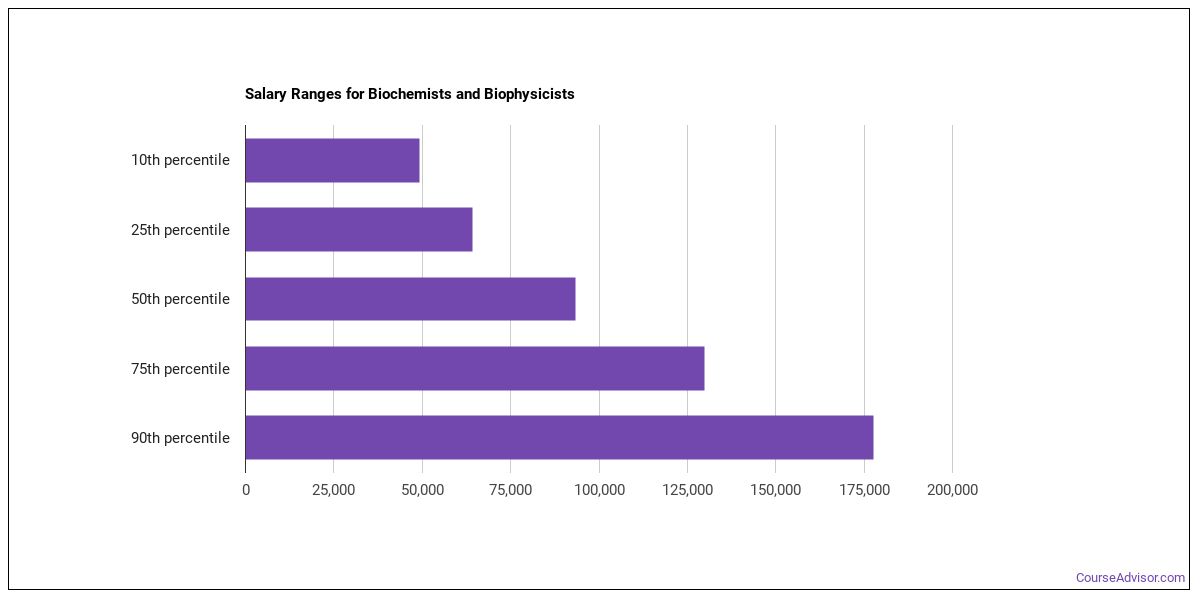
Potential earning

Managers in industrial plants oversee the smooth functioning of the whole process. They decide how to best utilize employees and equipment, meet production standards, and make strategic decisions. These people are responsible for evaluating and hiring workers. They also set production schedules and ensure safety. They monitor and evaluate the daily activities of a worker team.
The employer's experience and the earnings potential of industrial production managers will affect their earning potential. It's hard to predict future earnings for industrial managers. The average industrial production manager earned $103,380 annually in May 2016. Higher earnings may also be available for industrial production managers who have completed advanced training or certification. According to U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, those who have earned a bachelor’s or higher in industrial production management can earn more.
Environment for work
An industrial production manager splits time between the office and the production floor, sometimes in the same place. When working in a production area, industrial production managers must adhere to established safety and health practices. They often spend significant time in meetings and analysis of production data. They may also be responsible for writing reports. An industrial production manager's work environment can be dynamic.
Industrial production managers play a key role in a company's overall management structure. They coordinate the activities and improve productivity of different workers. An industrial production manager's primary responsibility is to increase productivity and ensure safety. Due to corporate restructuring, many levels have been eliminated and support staff reduced. Production managers are now able to handle more of the work load. This is a major challenge for any manager and can make the job difficult for a production manger.
FAQ
Is automation necessary in manufacturing?
Not only is automation important for manufacturers, but it's also vital for service providers. Automation allows them to deliver services quicker and more efficiently. It helps them to lower costs by reducing human errors, and improving productivity.
What does manufacturing mean?
Manufacturing Industries are businesses that produce products for sale. Consumers are those who purchase these products. These companies use various processes such as production, distribution, retailing, management, etc., to fulfill this purpose. These companies produce goods using raw materials and other equipment. This includes all types manufactured goods such as clothing, building materials, furniture, electronics, tools and machinery.
Do we need to know about Manufacturing Processes before learning about Logistics?
No. No. It is important to know about the manufacturing processes in order to understand how logistics works.
What are the responsibilities of a production planner
A production planner ensures all aspects of the project are delivered on time, within budget, and within scope. They make sure that the product and services meet client expectations.
Statistics
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use Lean Manufacturing for the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing (or lean manufacturing) is a style of management that aims to increase efficiency, reduce waste and improve performance through continuous improvement. It was developed by Taiichi Okono in Japan, during the 1970s & 1980s. TPS founder Kanji Takoda awarded him the Toyota Production System Award (TPS). Michael L. Watkins published the "The Machine That Changed the World", the first book about lean manufacturing. It was published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing is often described as a set if principles that help improve the quality and speed of products and services. It emphasizes the elimination and minimization of waste in the value stream. Just-in-time (JIT), zero defect (TPM), and 5S are all examples of lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing eliminates non-value-added tasks like inspection, rework, waiting.
Lean manufacturing is a way for companies to achieve their goals faster, improve product quality, and lower costs. Lean Manufacturing is one of the most efficient ways to manage the entire value chains, including suppliers and customers as well distributors and retailers. Lean manufacturing is widely practiced in many industries around the world. Toyota's philosophy is the foundation of its success in automotives, electronics and appliances, healthcare, chemical engineers, aerospace, paper and food, among other industries.
Five fundamental principles underlie lean manufacturing.
-
Define value - Find out what your business contributes to society, and what makes it different from other competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Remove any activity which doesn't add value to your supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize and Simplify – Make processes as consistent, repeatable, and as simple as possible.
-
Build Relationships- Develop personal relationships with both internal as well as external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing isn't a new concept in business, it has gained popularity due to renewed interest in the economy after the 2008 global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include improved customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels, lower operating costs, increased productivity, and better overall safety.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. This is because it ensures efficiency and effectiveness in all stages of the value chain.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing: This lean manufacturing method is commonly called "pull systems." JIT refers to a system in which components are assembled at the point of use instead of being produced ahead of time. This method reduces lead times, increases availability, and decreases inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM): ZDM focuses on ensuring that no defective units leave the manufacturing facility. You should repair any part that needs to be repaired during an assembly line. This is true even for finished products that only require minor repairs prior to shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.