
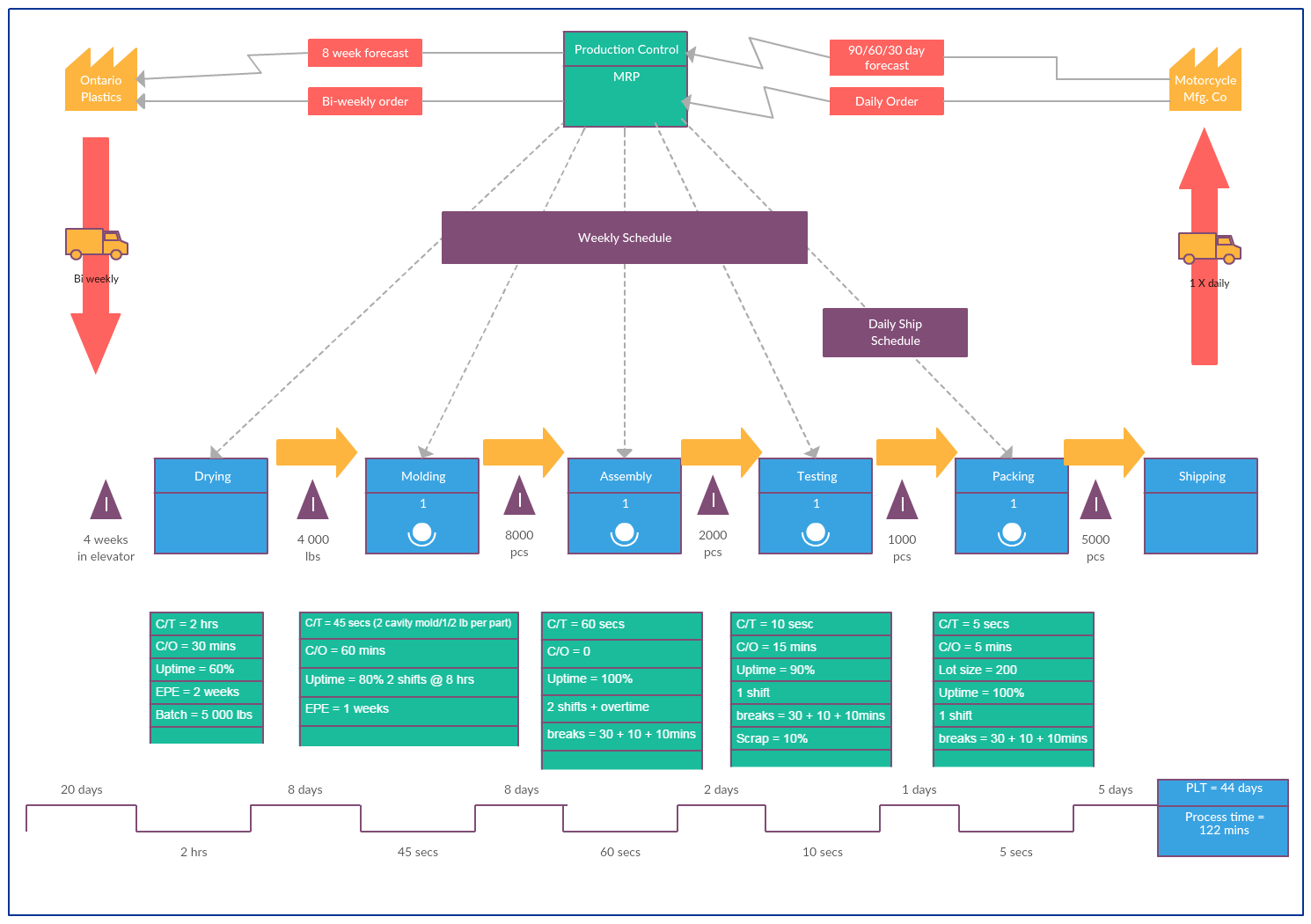
Using a single piece flow production line can increase your output while reducing your inventory and lead times. Before you start using this technology, here are some things to keep in mind. Measure the takt, which is how long it takes to produce an item. This will allow you to determine how fast you must produce an item in order to meet your customers' demands.
One piece flow is best suited to manufacturing operations that are geared towards low-variability products. However, this is not the best option for every business. To determine if this process is right for you, make sure that your metrics are accurate.
Choosing to use a single piece flow will also require a more robust and scalable control system. This will help to reduce waste and maximize efficiency. It is also important to ensure that the time required to make a single-piece item can be scaled to meet your customers' needs. This will ensure one-piece flow doesn't have a lower production efficiency than traditional manufacturing processes.
One-piece flow requires a production line with a U- or S-shaped shape. It will allow for less movement from one step to the next. It also increases assembly efficiency.
Poka-yoke is another term associated with lean. This clever method prevents defects from being moved to the next stage. This is a great way for you to save money and improve the quality your products. The poka-yoke also helps reduce waste and inefficiency.
This flow method is best used when there is a high need for individual products. This is when you don't want to waste time or money by mixing different items together from one order. A single flow for a work item will reduce delays and decrease inventory depreciation. It will also reduce the time products spend in the warehouse (WIP).
To reduce inventory maintenance costs, you can also use a single-piece flow process. This is especially true of small businesses. This allows you to cut down on the cost of inventory storage, transporting and repackaging your products. This is also a great way to reduce the amount of time you have to wait for your customers to receive your products.

One-piece flow also increases employee morale because it allows employees to collaborate more closely. This makes it easier for you to spot problems with your product. This is vital because it could lead to customers receiving defective or incomplete products. This is a great opportunity to improve your customer service.
An assembly line can have a one-piece flow line. This process can be used to optimize your value stream. This allows for quicker production and better quality products. It can also be a great way of reducing costs and boosting morale among employees.
FAQ
What does it mean to be a manufacturer?
Manufacturing Industries refers to businesses that manufacture products. Consumers are those who purchase these products. This is accomplished by using a variety of processes, including production, distribution and retailing. They create goods from raw materials, using machines and various other equipment. This includes all types of manufactured goods, including food items, clothing, building supplies, furniture, toys, electronics, tools, machinery, vehicles, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, chemicals, and many others.
What are the differences between these four types?
Manufacturing refers the process of turning raw materials into useful products with machines and processes. It includes many different activities like designing, building and testing, packaging, shipping and selling, as well as servicing.
How can I find out more about manufacturing?
Practical experience is the best way of learning about manufacturing. But if that is not possible you can always read books and watch educational videos.
What is the difference between Production Planning, Scheduling and Production Planning?
Production Planning (PP), also known as forecasting and identifying production capacities, is the process that determines what product needs to be produced at any particular time. Forecasting demand is one way to do this.
Scheduling is the process of assigning specific dates to tasks so they can be completed within the specified timeframe.
What is manufacturing and logistics?
Manufacturing refers the process of producing goods from raw materials through machines and processes. Logistics is the management of all aspects of supply chain activities, including procurement, production planning, distribution, warehousing, inventory control, transportation, and customer service. Sometimes manufacturing and logistics are combined to refer to a wider term that includes both the process of creating products as well as their delivery to customers.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use lean manufacturing in the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing refers to a method of managing that seeks to improve efficiency and decrease waste. It was first developed in Japan in the 1970s/80s by Taiichi Ahno, who was awarded the Toyota Production System (TPS), award from KanjiToyoda, the founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the first book on lean manufacturing in 1990.
Lean manufacturing can be described as a set or principles that are used to improve quality, speed and cost of products or services. It is about eliminating defects and waste from all stages of the value stream. Lean manufacturing is also known as just in time (JIT), zero defect total productive maintenance(TPM), and five-star (S). Lean manufacturing eliminates non-value-added tasks like inspection, rework, waiting.
Lean manufacturing can help companies improve their product quality and reduce costs. Additionally, it helps them achieve their goals more quickly and reduces employee turnover. Lean Manufacturing is one of the most efficient ways to manage the entire value chains, including suppliers and customers as well distributors and retailers. Many industries worldwide use lean manufacturing. Toyota's philosophy, for example, is what has enabled it to be successful in electronics, automobiles, medical devices, healthcare and chemical engineering as well as paper and food.
Lean manufacturing includes five basic principles:
-
Define value - Find out what your business contributes to society, and what makes it different from other competitors.
-
Reduce waste - Stop any activity that isn't adding value to the supply chains.
-
Create Flow - Ensure work moves smoothly through the process without interruption.
-
Standardize and Simplify – Make processes as consistent, repeatable, and as simple as possible.
-
Build Relationships - Establish personal relationships with both internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing isn’t new, but it has seen a renewed interest since 2008 due to the global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. In fact, some economists believe that lean manufacturing will be an important factor in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is becoming a popular practice in automotive. It has many advantages. These include better customer satisfaction and lower inventory levels. They also result in lower operating costs.
It can be applied to any aspect of an organisation. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three main types:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing (JIT), also known as "pull system": This form of lean manufacturing is often referred to simply as "pull". JIT means that components are assembled at the time of use and not manufactured in advance. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing, (ZDM): ZDM is focused on ensuring that no defective products leave the manufacturing facility. Repairing a part that is damaged during assembly should be done, not scrapping. This applies to finished products, which may need minor repairs before they are shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI: Continuous improvement aims to increase the efficiency of operations by constantly identifying and making improvements to reduce or eliminate waste. Continuous improvement involves continuous improvement of processes and people as well as tools.